How does aliasing occur in rasterization?
Below is a test image to be rasterized. There is a black line, a big green and a small magenta circle.
To rasterize it, the image is sampled at regular intervals. The sampling points are represented as red pixels:
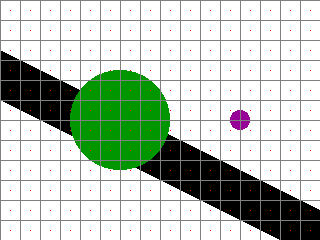
When these sampling points are rendered as an image, the result is as follows:
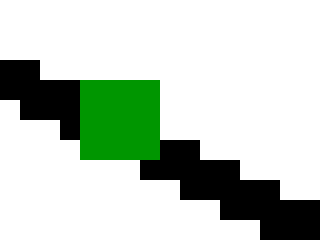
Aliasing artifacts are clearly visible. It is also quite noticeable that the magenta circle is not rendered in the final image, because its size falls below the sampling grid resolution. If the sampling resolution is increased, we get a higher density of sampling points.
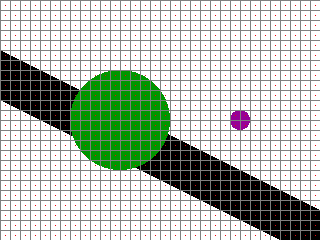
and the rendered result:
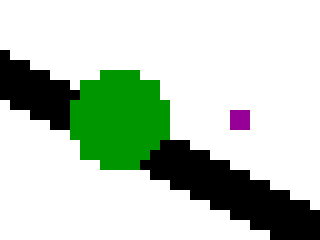
This reduces the staircase effect (aliasing artifacts) and the magenta circle is also visible.